| only for RuBoard - do not distribute or recompile |
There are four types of HTTP headers:
General headers indicate general information such as the date, or whether the connection should be maintained. They are used by both clients and servers.
Request headers are used only for client requests. They convey the client's configuration and desired document format to the server.
Response headers are used only in server responses. They describe the server's configuration and information about the requested URL.
Entity headers describe the document format of the data being sent between client and server. Although Entity headers are most commonly used by the server when returning a requested document, they are also used by clients when using the POST or PUT methods.
Headers from all four categories may be specified in any order. Header names are case-insensitive, so the Content-type header is also frequently written as Content-type.
General headers are used in both client requests and server responses. Some may be more specific to either a client or server message.
| Cache-Control: directives |
The Cache-control header specifies desired behavior from a caching system, as used in proxy servers. For example:
Cache-control: no-cache
Both clients and servers can use the Cache-control header to specify parameters for the cache or to request certain kinds of documents from the cache. The caching directives are specified in a comma-separated list.
Cache request directives are:
|
Directive |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
no-cache |
A cache can keep a cached copy of the document, but must always revalidate it before sending it back to the client. |
|
no-store |
Remove information promptly after forwarding. The cache should not store anything about the client request or server response. This option prevents the accidental storing of secure or sensitive information in the cache. |
|
max-age = seconds |
Do not send responses older than seconds. The cache can send a cached document that has been retrieved within a certain number of seconds from the time it was sent by the origin server. |
|
max-stale [ = seconds ] |
The cache can send a cached document that is older than its expiration date. If seconds are given, it must not be expired by more than that time. |
|
min-fresh = seconds |
Send data only if still fresh after the specified number of seconds. The cache can send a cached document only if there are at least a certain number of seconds between now and its expiration time. |
|
only-if-cached |
Do not retrieve new data. The cache can send a document only if it is in the cache, and should not contact the origin-server to see if a newer copy exists. This option is useful when network connectivity from the cache to origin-server is poor. |
Cache response directives are:
|
Directive |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
public |
The document is cacheable by any cache. |
|
private |
The document is not cacheable by a shared cache. |
|
no-cache |
A cache can keep a cached copy of the document, but must always revalidate it before sending it back to the client. |
|
no-store |
Do not store the returning document. Remove information promptly after forwarding. |
|
no-transform |
Do not convert the entity-body. Useful for applications that require that the message received is exactly what was sent by the server. |
|
must-revalidate |
The cache must verify the status of stale documents, i.e., the cache cannot blindly use a document that has expired. |
|
proxy-revalidate |
Client must revalidate data except for private client caches. Public caches must verify the status of stale documents. Like must-revalidate, excluding private caches. |
|
max-age = seconds |
The document should be considered stale in the specified number of seconds from the time of retrieval. |
|
s-maxage = seconds |
The same as max-age, except for public/shared caches. This directive is ignored by private caches. |
| Connection: options |
Specifies options desired for this connection but not for further connections by proxies. For example:
Connection: close
The close option signifies that either the client or server wishes to end the connection (i.e., this is the last transaction). The keep-alive option signifies that the client wishes to keep the connection open. The default behavior of web applications differs between HTTP 1.0 and 1.1.
By default, HTTP 1.1 uses persistent connections, where the connection does not automatically close after a transaction. When an HTTP 1.1 web client no longer has any requests, or the server has reached some preprogrammed limit in spending resources on the client, a Connection: close header indicates that no more transactions will proceed, and the connection closes after the current one. An HTTP 1.1 client or server that doesn't support persistent connections should always use the Connection: close header.
HTTP 1.0, on the other hand, does not have persistent connections by default. If a 1.0 client wishes to use persistent connections, it uses the keep-alive parameter. A Connection: keep-alive header is issued by both HTTP 1.0 clients and servers for each transaction under persistent connections. The last transaction does not have a Connection: keep-alive header, and behaves like a Connection: close header under HTTP 1.1. HTTP 1.0 servers that do not support persistent connections will not have a Connection: keep-alive header in their response, and the client should disconnect after the first transaction completes.
Use of the keep-alive parameter is known to cause problems with proxy servers that do not understand persistent connections for HTTP 1.0. If a proxy server blindly forwards the Connection: keep-alive header, the origin-server and initial client are using persistent connections while the proxy server is not. The origin server maintains the network connection when the proxy server expects a disconnect; timing problems follow.
To get around that, when HTTP 1.1 proxies encounter an HTTP 1.0 request, it must remove the Connection header and any headers specified by the Connection header before forwarding the message.
| Date: dateformat |
There are three formats that can be used to express the date. The preferred date format is RFC 1123. For example:
Mon, 06 May 1996 04:57:00 GMT
The preferred RFC 1123 format specifies all dates in a fixed length string in Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). GMT is always used in HTTP to prevent any misunderstandings among computers communicating in different time zones. The valid days are: Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, and Sun. The months are: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, and Dec.
For backwards compatibility, the RFC 1036 and ANSI C asctime ( ) formats are also acceptable, but not recommended:
Monday, 06-May-96 04:57:00 GMT
Mon May 6 04:57:00 1996
The RFC 1036 format is similar to the one in RFC 1123, except that the string length varies, depending on the day of the week, and the year is specified in two digits instead of four. This makes date parsing more difficult. The valid days are: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday, Sunday. The months are: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, and Dec.
ANSI C's asctime ( ) format is not encouraged, since there can be misunderstandings about the time zone used by the computer. The valid days are: Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, and Sun. The months are: Jan, Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sep, Oct, Nov, and Dec.
Despite a heavy preference for RFC 1123's format, current web clients and servers should be able to recognize all three formats. However, when designing web programs, it is desirable to use RFC 1123 when generating dates. Future versions of HTTP may not support the latter two formats.
| Pragma: no-cache |
The Pragma header specifies directives for proxy and gateway systems. Since many proxy systems may exist between a client and server, Pragma headers must pass through each proxy. When the Pragma header reaches the server, the header may be ignored by the server software.
The only directive defined in HTTP/1.0 is the no-cache directive. It is used to tell caching proxies to contact the server for the requested document, instead of using its local cache. This allows the client to request the most up-to-date document from the original web server, without receiving a cached copy from an intermediate proxy server.
The Pragma header is an HTTP 1.0 feature, and is maintained in HTTP 1.1 for backward compatibility. No new Pragma directives will be defined in the future.
Example:
Pragma: no-cache
| Trailer: trailer_headers |
The Trailer header specifies the headers in the trailer of a chunked message. This header is not used if there are no headers specified after a chunked message. Also, it is not possible to expect Transfer-Encoding, Content-Length, or Trailer as a trailer header.
| Transfer-Encoding: encoding_type |
The Transfer-Encoding header specifies that the message is encoded. This is not the same as content-encoding (an entity-body header, discussed later), since transfer-encodings are a property of the message, not of the entity-body. For example:
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
In the HTTP 1.1 specification, chunked is the only encoding method supported.
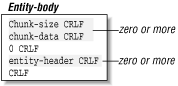
The chunked transfer-encoding encodes the message as a series of chunks followed by entity-headers, as shown in Figure 1.6. The chunks and entity-headers are in a client's request entity-body or server response entity-body. Each chunk contains a chunk size specified in base 16, followed by CRLF. After that, the chunk body, whose length is specified in the chunk size, is presented, followed by a CRLF. Consecutive chunks are specified one after another, with the last chunk having a length of zero followed by CRLF. Entity-headers follow the chunks, terminated by a CRLF on a line by itself.
| Upgrade: protocol/version |
Using the Upgrade header, the client can specify additional protocols that it understands, and that it would prefer to talk to the server with an alternate protocol. If the server wishes to use the alternate protocol, it returns a response code of 101 and indicates which protocol it is upgrading to, with the Upgrade header. After the terminating CRLF in the server's header response, the protocol switches.
Portion of client request:
Upgrade: HTTP/1.2
Portion of server response:
HTTP/1.1 101 Upgrading Protocols
Upgrade: HTTP/1.2
| Via: protocol host |
The Via header is updated by proxy servers as messages pass from client to server and from server to client. Each proxy server appends its protocol and protocol version, hostname, port number, and comment to a comma-separated list on the Via header. If the Via header does not exist, the first proxy creates it. This information is useful for debugging purposes. If the protocol name is HTTP, it can be omitted. For HTTP, a port number of 80 can be omitted. Comments are optional.
Example:
Via: 1.1 proxy.ora.com, 1.0 proxy.internic.gov
See the discussion of the TRACE method for more details.
| Warning: code host string |
Indicates information additional to that in the status code, for use by caching proxies. For example:
Warning: Response stale
The host field contains the name or pseudonym of the server host, with an optional port number. The two-digit warning codes and their recommended descriptive strings are:
|
Code |
String |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
110 |
Response stale |
The response data is known to be stale. |
|
111 |
Revalidation failed |
The response data is known to be stale because the proxy failed to revalidate the data. |
|
112 |
Disconnected operation |
The cache is disconnected from the network. |
|
113 |
Heuristic expiration |
The data is older than 24 hours, and the cache heuristically chose a freshness lifetime greater than 24 hours. |
|
199 |
Miscellaneous warning |
Arbitrary information to be logged or presented to the user. |
|
214 |
Transformation applied |
The proxy has changed the encoding or media type of the document, as specified by the Content-Encoding or Content-Type headers. |
|
299 |
Miscellaneous persistent warning |
Arbitrary persistent information to be logged or presented to the user. |
Client header data communicates the client's configuration and preferred document formats to the server. Request headers are used in a client message to provide information about the client.
| Accept: type/subtype [q=qvalue] |
Specifies media types the client prefers to accept. For example:
Accept: text/*, image/gif
Multiple media types can be listed separated by commas. The optional qvalue represents, on a scale of to 1, an acceptable quality level for accept types.
| Accept-Charset: character_set [q=qvalue] |
Specifies the character sets that the client prefers. Multiple character sets can be listed separated by commas. The optional qvalue represents, on a scale of to 1, an acceptable quality level for nonpreferred character sets. If this header is not specified, the server assumes the default of US-ASCII and ISO-8859-1 (a superset of US-ASCII), which are both specified in RFC 1521. For example:
Accept-charset: ISO-8859-7
| Accept-Encoding: encoding_types |
Through the Accept-Encoding header, a client may specify what encoding algorithms it understands. If this header is omitted, the server will send the requested entity-body without any additional encoding. Encoding mechanisms can be used to reduce consumption of scarce resources, at the expense of less expensive resources. For example, large files may be compressed to reduce transmission time over slow network connections.
In the HTTP/1.0 specification, two encoding mechanisms are defined: x-gzip and x-compress. Multiple encoding schemes can be listed, separated by commas. For reasons of compatibility with historical practice, gzip and compress should be considered the same as x-gzip and x-compress.
|
Encoding Mechanism |
Encoded By |
|---|---|
|
gzip |
Jean-Loup Gailly's GNU zip compression scheme |
|
compress |
Modified Lempel-Ziv compression scheme |
|
deflate |
The deflate method found in PKWARE products |
For example:
Accept-encoding: gzip
There is no guarantee that the requested encoding mechanism has been applied to the entity-body returned by the server. If the client specifies an Accept-encoding header, it should examine the server's Content-encoding header to see if an encoding mechanism was applied. If the Content-encoding header has been omitted, no encoding mechanism was applied.
| Accept-Language: language [q=qvalue] |
Specifies the languages that the client prefers. If a client wants to specify a preference for a particular language, it is done in the Accept-Language header. If a server contains the same document in multiple languages, it will send the document in the language of the client's preference, when available. For example:
Accept-language: en
Multiple languages can be listed separated by commas. The optional qvalue represents, on a scale of to 1, an acceptable quality level for nonpreferred languages. Languages are written with their two-letter abbreviations (e.g., en for English, de for German, fr for French, etc.).
| Authorization: scheme credentials |
Provides the client's authorization to access data at a URL. When a requested document requires authorization, the server returns a WWW-Authenticate header describing the type of authorization required. The client then repeats the request with the proper authorization information.
The HTTP/1.0 specification defines the BASIC authorization scheme, where the authorization parameter is the string of username:password encoded in base 64. For example, for the username of webmaster and a password of zrma4v, the authorization header would look like this:
Authorization: BASIC d2VibWFzdGVyOnpycW1hNHY=
The value decodes into webmaster:zrma4v.
| Cookie: name=value |
Contains a name/value pair of information stored for that URL. For example:
Cookie: acct=03847732
Multiple cookies can be specified, separated by semicolons. For browsers supporting cookies, see Section 1.11 later in this book for more information.
An issue arises with proxy servers in regard to the headers. Set-Cookie and Cookie headers both should be propagated through the proxy, even if a page is cached or has not been modified (according to the If-Modified-Since condition). The Set-Cookie header should never be cached by the proxy.
| Expect: expectation |
This header indicates a client expectation about the server. If the server is not capable of the expectation, it returns a status code of 417 (Expectation Failed). The expectation must be met for all intermediate servers as well. All proxies, as well as the origin server must meet the expectation or return status code of 417.
| From: email_address |
Gives the email address of the user executing the client. The From header helps the server identify the source of malformed requests or excessive resource usage. For example:
From: webmaster@www.ora.com
This header should be sent when possible, but should not be sent without the user's consent, in the interest of privacy. However, when running clients that use excessive network or server resources, it is advisable to include this header, in the event that an administrator would like to contact the client user.
| Host: hostname: port |
The hostname and optional port number of the server contacted by the client. If the port number is 80, the colon and port number should be omitted. For example:
Host: www.ora.com
Or for a port number other than 80 (in this example, 7777):
Host: www.ora.com:7777
This is useful to indicate what server the client thinks it is talking to. It allows multihomed servers to use the same IP address with different DNS names. Clients must supply this information in HTTP 1.1, so servers with multiple hostnames can easily differentiate between ambiguous URLs.
| If-Modified-Since: date |
Specifies that the URL data is to be sent only if it has been modified since the date given as the value of this header. This is useful for client-side caching. For example:
If-Modified-Since: Mon, 04 May 1996 12:17:34 GMT
If the document has not been modified, the server returns a code of 304, indicating that the client should use the local copy. The specified date should follow the format described under the Date header.
| If-Match: entity_tag |
A conditional requesting the entity only if it matches the given entity tags (see the ETag entity header). An asterisk (*) matches any entity, and the transaction continues only if the entity exists.
| If-None-Match: entity_tag |
A conditional requesting the entity only if it does not match any of the given entity tags (see the ETag entity header). An asterisk (*) matches any entity; if the entity doesn't exist, the transaction continues.
| If-Range: (entity_tag | date) |
A conditional requesting only the portion of the entity that is missing, if it has not been changed, and the entire entity if it has. Used in conjunction with the Range header to indicate the entity tag or last modified time of a document on the server. For example:
If-Range: Mon, 04 May 1996 12:17:34 GMT
If the document has not been modified, the server returns the byte range given by the Range header; otherwise, it returns all of the new document. Either an entity tag or a date can be used to identify the partial entity already received; see the Date header for information on the format for dates.
| If-Unmodified-Since: date |
Specifies that the entity-body should be sent only if the document has not been modified since a given date. For example:
If-Unmodified-Since: Tue, 05 May 1996 04:03:56 GMT
The specified date should follow the format described under the Date header.
| Max-Forwards: n |
Limits the number of proxies or gateways that can forward the request. Useful for debugging with the TRACE method, avoiding infinite loops. For example:
Max-Forwards: 3
A proxy server that receives a Max-Forwards value of zero (0) should return the request headers to the client in its response entity-body. See the discussion of the TRACE method for more details.
| Proxy-Authorization: credentials |
For a client to identify itself to a proxy requiring authorization.
| Range: bytes=n-m |
Specifies the partial range(s) requested from the document. For example:
Range: bytes=1024-2047,4096-
Multiple ranges can be listed, separated by commas. If the first digit in the comma-separated byte range(s) is missing, the range is assumed to count from the end of the document. If the second digit is missing, the range is byte n to the end of the document. The first byte is byte 0.
| Referer: url |
Gives the URL of the document that refers to the requested URL (i.e., the source document of the link). For example:
Referer: http://www.yahoo.com/Internet/
| TE: transfer-codings |
This header specifies a comma separated list of the transfer-codings it is willing to accept. For example, to indicate that trailer fields in a chunked transfer-coding are acceptable:
TE: trailers
| User-Agent: string |
Gives identifying information about the client program. Here is an example:
User-Agent: Mozilla 3.0b
The response headers described here are used in server responses to communicate information about the server and how it may handle requests.
| Accept-Ranges: bytes|none |
Indicates the acceptance of range requests for a URL, specifying either the range unit (e.g., bytes) or none if no range requests are accepted. For example:
Accept-Ranges: bytes
| Age: seconds |
Indicates the age of the document in seconds. For example:
Age: 3521
| ETag: entity_tag |
This header specifies the entity tag for the requested server resource. The entity tag is a unique identifier associated with the server resource and can be used for caching purposes. The entity tag can then be used with the If-Match and If-None-Match request headers.
| Location: url |
Specifies the new location of a document, usually with response code 201 (Created), 301 (Moved Permanently), 302 (Found), 303 (See Other), or 307 (Moved Temporarily). The URL given must be written as an absolute URL. For example:
Location: http://www.ora.com/contacts.html
| Proxy-Authenticate: scheme realm |
Indicates the authentication scheme and parameters applicable to the proxy for this URL and the current connection. Used with response 407 (Proxy Authentication Required).
| Retry-After: date|seconds |
Specifies a time when the server can handle requests. Used with response code 503 (Service Unavailable). It contains either an integer number of seconds or a GMT date and time (as described by the Date header formats). If the value is an integer, it is interpreted as the number of seconds to wait after the request was issued. For example:
Retry-After: 3600
Retry-After: Sat, 18 May 1996 06:59:37 GMT
| Server: string |
Contains the name and version number of the server. For example:
Server: NCSA/1.3
| Set-Cookie: name=value options |
Contains a name/value pair of information to retain for this URL. For browsers supporting cookies. For example:
Set-Cookie: acct=03845324
Options are:
|
Option |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
expires = date |
The cookie becomes invalid after the specified date. |
|
path = pathname |
The URL range for which the cookie is valid. |
|
domain = domain_name |
The domain name range for which the cookie is valid. |
|
secure |
Return the cookie only under a secure connection. |
| Vary: headers |
Specifies that the entity has multiple sources and may therefore vary according to specified list of request header(s).
Vary: Accept-Language,Accept-Encoding
Multiple headers can be listed, separated by commas. An asterisk (*) means that another factor, other than the request headers, may affect the document that is returned.
| WWW-Authenticate: scheme realm |
A request for authentication, used with the 401 (Unauthorized) response code. It specifies the authorization scheme and realm of authorization required from a client at the requested URL. Many different authorization realms can exist on a server. A common authorization scheme is BASIC, which requires a username and password. For example:
WWW-Authenticate: BASIC realm="Admin"
When returned to the client, this header indicates that the BASIC type of authorization data in the appropriate realm should be returned in the client's Authorization header.
Another scheme is Digest, which improves security by not transmitting the password as cleartext. The BASIC and Digest schemes are described in RFC 2617. Unfortunately, Digest is not widely used, given that not all browsers support it.
Windows-based HTTP servers sometimes use a scheme called NTLM. It isn't as widely used as BASIC as well, given that not all browsers implement the NTLM scheme.
Entity headers are used in both client requests and server responses. They supply information about the entity body in an HTTP message.
| Allow: methods |
Contains a comma-separated list of methods that are allowed at a specified URL. In a server response it is used with code 405 (Method Not Allowed) to inform the client of valid methods available for the requested information. For example:
Allow: GET, HEAD
Some methods may not apply to a URL, and the server must verify that the methods supplied by the client makes sense with the given URL.
| Content-Encoding: encoding_schemes |
Specifies the encoding scheme(s) used for the transferred entity-body. Values are gzip (or x-gzip) and compress (or x-compress). If multiple encoding schemes are specified (in a comma-separated list), they must be listed in the order in which they were applied to the source data.
The server should attempt to use an encoding scheme used by the client's Accept-Encoding header. The client may use this information to determine how to decode the document after it is transferred.
See the description of the Accept-Encoding header earlier in this appendix for a listing of possible values. For example:
Content-Encoding: x-gzip
| Content-Language: languages |
Specifies the language(s) that the transferred entity-body is intended for. Languages are represented by their two-letter abbreviations (e.g., en for English, fr for French). The server should attempt to use a language specified by the client's Accept-Language header. This header is useful when a client specifies a preference for one language over another for a given URL. For example:
Content-Language: fr
| Content-Length: n |
This header specifies the length of the data (in bytes) of the transferred entity-body. For example:
Content-Length: 47293
Due to the dynamic nature of some requests, the content length is sometimes unknown and this header is omitted.
| Content-Location: url |
Supplies the URL for the entity, in cases where a document has multiple entities with separately accessible locations. The URL can be either an absolute or relative URL. For example:
Content-Location: http://www.ora.com/products/
See Section 1.9 later in this book.
| Content-MD5: digest |
Supplies an MD5 digest of the entity, for checking the integrity of the message upon receipt. For example:
Content-MD5: d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e
| Content-Range: bytes n-n/m |
Specifies where the accompanying partial entity-body should be inserted, and the total size of the full entity-body. For example:
Content-Range: bytes 6143-7166/15339
| Content-Type: type/subtype |
Describes the media type and subtype of an entity-body. It uses the same values as the client's Accept header, and the server should return media types that conform with the client's preferred formats. For example:
Content-type: text/html
| Expires: date |
Specifies the time when a document may change, or when its information becomes invalid. After that time, the document may or may not change or be deleted. The value is a date and time in a valid format as described for the Date header. For example:
Expires: Sat, 20 May 1995 03:32:38 GMT
This is useful for cache management. The Expires header means it is unlikely that the document will change before the given time. This does not imply that the document will be changed or deleted at that time. It is only an advisory that the document will not be modified until the specified time.
| Last-Modified: date |
Specifies when the URL was last modified. The value is a date and time in a valid format as described for the Date header. If a client has a copy of the URL in its cache that is older than the last-modified date, it should be refreshed. For example:
Last-Modified: Sat, 20 May 1995 03:32:38 GMT
The following is a listing of all HTTP headers supported by each version of HTTP so far.
|
Method |
General |
Request |
Entity |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GET |
None |
None |
None |
None |
|
Method |
General |
Request |
Entity |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GET |
Connection |
Accept |
Allow |
Location |
|
HEAD |
Date |
Accept-charset |
Content-encoding |
Retry-after |
|
POST |
MIME-version |
Accept-encoding |
Content-language |
Server |
|
PUT |
Pragma |
Accept-language |
Content-length |
WWW-Authenticate |
|
DELETE |
Authorization |
Content-type |
||
|
LINK |
From |
Expires |
||
|
UNLINK |
If-modified-since |
Last-modified |
||
|
Referer |
Link |
|||
|
User-agent |
Title |
|||
|
URL |
|
Method |
General |
Request |
Entity |
Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
OPTIONS |
Cache-control |
Accept |
Allow |
Accept-Ranges |
|
GET |
Connection |
Accept-charset |
Content-encoding |
Age |
|
HEAD |
Date |
Accept-encoding |
Content-language |
Etag |
|
POST |
Pragma |
Accept-language |
Content-length |
Location |
|
PUT |
Trailer |
Authorization |
Content-location |
Proxy-authenticate |
|
DELETE |
Transfer-encoding |
Expect |
Content-md5 |
Retry-after |
|
TRACE |
Upgrade |
From |
Content-range |
Server |
|
CONNECT |
Via |
Host |
Content-type |
Vary |
|
Warning |
If-modified-since |
Expires |
WWW-Authenticate |
|
|
If-match |
Last-modified |
|||
|
If-none-match |
||||
|
If-range |
||||
|
If-unmodified-since |
||||
|
Max-forwards |
||||
|
Proxy-authorization |
||||
|
Range |
||||
|
Referer TE |
||||
|
User-agent |
| only for RuBoard - do not distribute or recompile |